 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
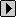
Taxonomic attribute-values
For attributes which values are structured by relations of hierarchical type (classified values), an extension of the discrete classifier partitioning process is proposed.
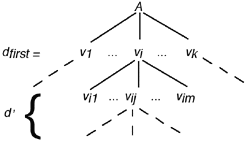
Fig. 4. Classified values of attribute A
The method consists, when such a classifier is selected, in creating a set of partitions corresponding to the first level of the hierarchy (noted dfirst = {v1,..., vi,..., vk} with k elements). Each case is assigned to the partition that generalizes its value. Let A be a taxonomic attribute with the domain d = {v1,..., vi,..., vn} of n modalities andis a subtree of m submodalities of vi [Fig. 4]:
Let Q be a Boolean application (called question) which determines if the modality vi generalizes a value vij. Q is defined by:
Then, we can generate k partitions from dfirst:
In the next step, we create temporarily k attributes {A1,..., Aj,..., Ak} in each partition EA1,..., EAk with a set of modalities defined by the subvalues of {v1,..., vi,..., vk}. These ones can be picked by the test function (information gain, gain ratio) and the method is recursively reapplied.
Multi-valued attributes
When modeling the descriptive model, a discrete attribute (nominal or taxonomic) can be defined as multi-valued. It can express doubt (disjunction of imprecision) or the simultaneous presence of states (conjunction of variation) like in the following expression:
v = (v11 & ... v1i ... & v1m) | ... | (vj1 & ... vji ... & vjn) | ... | (vk1 & ... vki ... & vkp) where cfi = (vj1 & ... vji ... & vjn)
Depending on the semantic associated with a conjunctive form of a case (cf), IKBS can apply three processing methods:
- If cf is true information (association of co-existing facts), create k partitions corresponding to each conjunction of v, and dispatch cases with such value in each partition: cf is seen as a new possible value of dom(A).
- If cf expresses fuzzy information (the intrinsic variability of multiple objects is an adding source of noise), treat conjunctions as disjunction.
- Allow the user to customize the degree of similarity
between two conjunctive forms.
The default method is the third one with = 1 because it gives a good compromise between the tree size (number of nodes) and the discrimination accuracy. Indeed, the first method don't generate a deep tree, but carries a major risk of misidentification: each cf of the selected attribute at a node of the decision tree must match exactly the cf of the tested case. The third method is more flexible because it makes a fuzzy matching for dispatching cases in each partition, depending on the number of differences between the two conjunctive forms and
.