 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
280 |
|||||||||||
|
Annexe 5 |
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
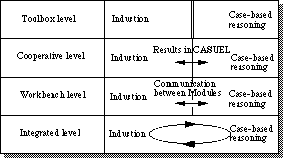
Figure 2. Four integration levels between Kate and Patdex |
|||||||||||
|
6. An integration architecture to handle missing values efficiently As stated in section 3, one main drawback of a decision tree consultation occurs if the user
|
|||||||||||
|
Procedure for Switching between Kate and Patdex |
|||||||||||
|
This procedure combines the advantages of both techniques for efficiency and correctness. In
Induction and case-based reasoning are complementary approaches for developing experience-
|
|||||||||||